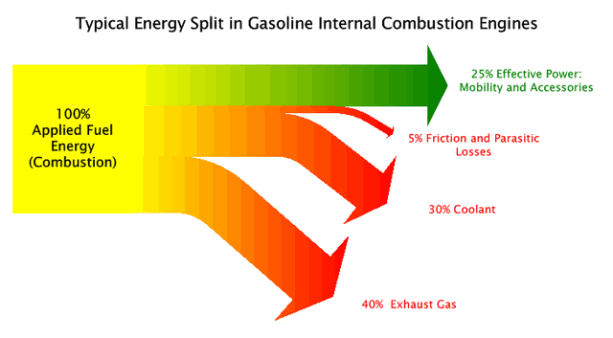
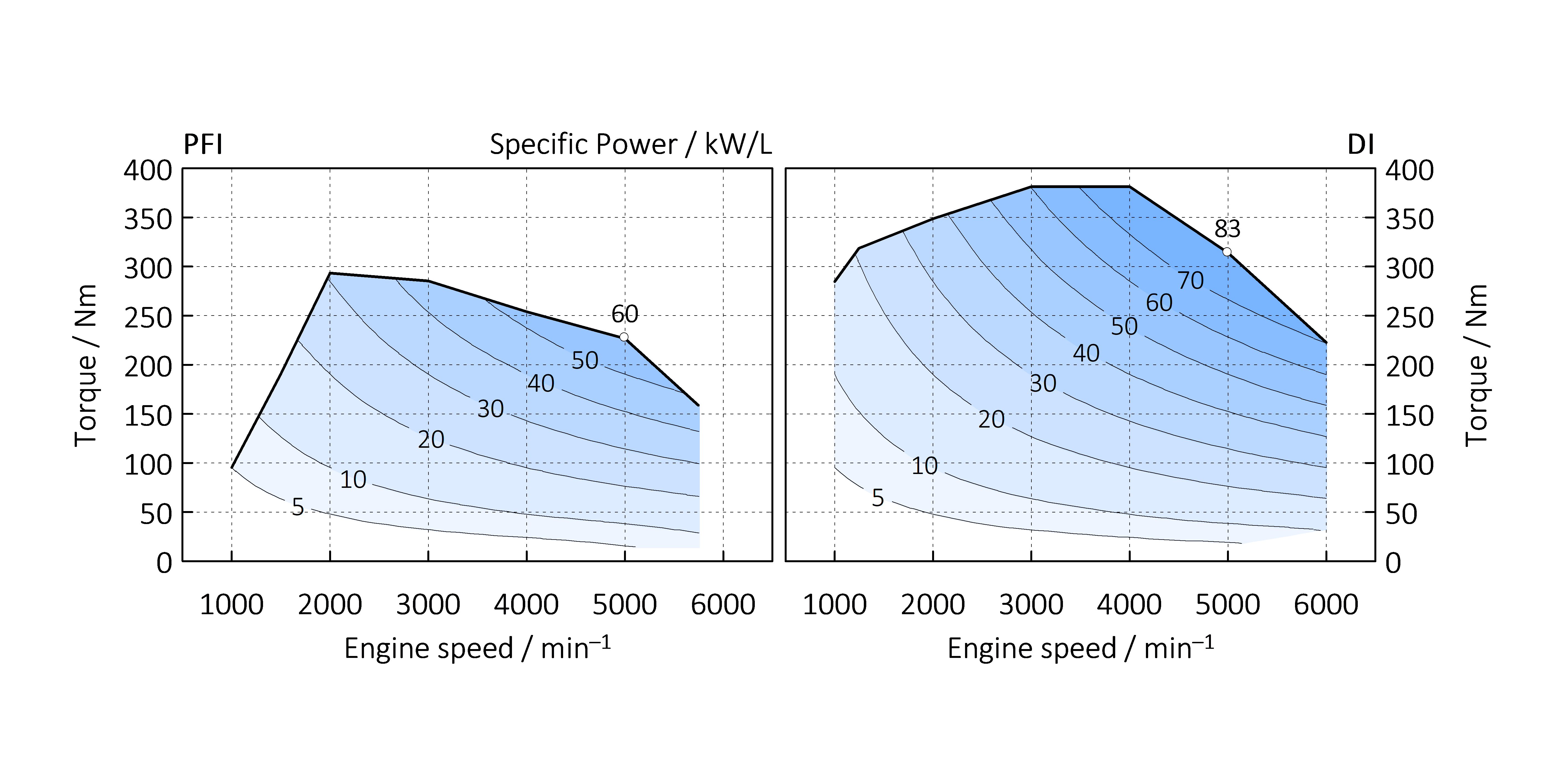
The conversion of fuel energy into useful work in an internal combustion engine involves a number of loses.
Energy conversion efficiency of internal combustion engine.
Internal combustion engine the internal combustion engine the motor of the early 20th century economy has brought far reaching changes to society that enabled convenient and affordable individual transportation.
Tank to wheel efficiency includes the entire efficiency chain from the energy storage e g.
Where the energy goes.
In such a device a fuel and oxidizer are burned within the engine and.
Most internal combustion engines are incredibly inefficient at turning fuel burned into usable energy.
They have achieved an energy conversion efficiency of 54 4.
The engine consists of a fixed cylinder and.
While the steam engine remained dominant in industry and transportation during much of the 19th century engineers and scientists began developing other sources and converters of energy.
The efficiency by which they do so is measured in terms of thermal efficiency and most.
In an internal combustion engine ice the ignition and combustion of the fuel occurs within the engine itself.
External combustion engines steam piston steam turbine and the stirling cycle engine.
Engine efficiency of thermal engines is the relationship between the total energy contained in the fuel and the amount of energy used to perform useful work there are two classifications of thermal engines internal combustion gasoline diesel and gas turbine brayton cycle engines and.
Only about 12 30 of the energy from the fuel you put in a conventional vehicle is used to move it down the road depending on the drive cycle the rest of the energy is lost to engine and driveline inefficiencies or used to power accessories.
Engines in newer diesel cars buses and large diesel trucks can attain a maximum efficiency of 45.
The engine then partially converts the energy from the combustion to work.
The major engine energy losses and the corresponding efficiency factors are illustrated in figure 1 3038.
An internal combustion engine ice is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer usually air in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit.
In an internal combustion engine the expansion of the high temperature and high pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine.
Combustion engine plus the mentioned.
These days turbo diesel engines increase their efficacy by using electronically controlled common rail fuel injection.
Combustion also known as burning is the basic chemical process of releasing energy from a fuel and air mixture.
Energy conversion energy conversion internal combustion engines.
Fuel in the tank the energy conversion in the engine e g.
Overview of energy losses in a typical internal combustion engine.