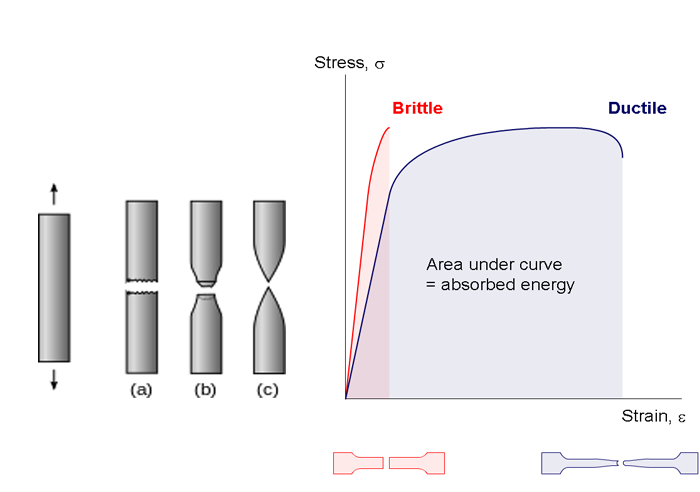
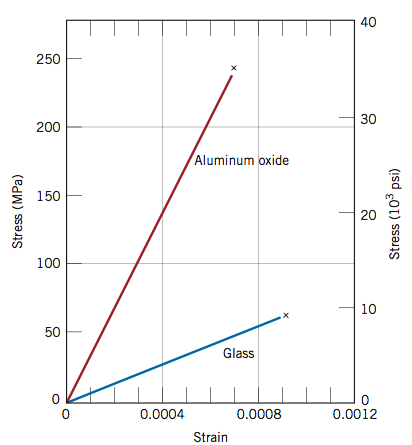
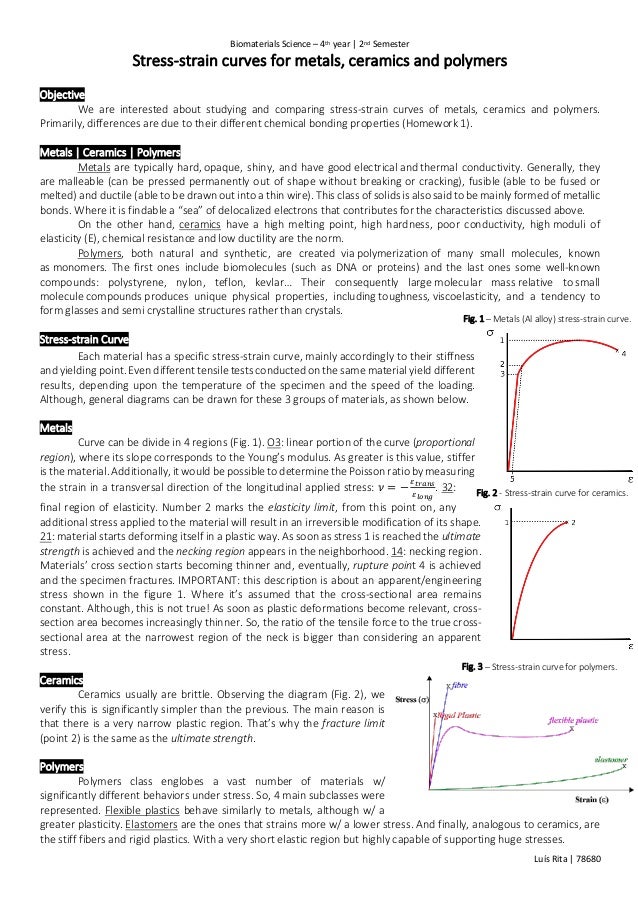
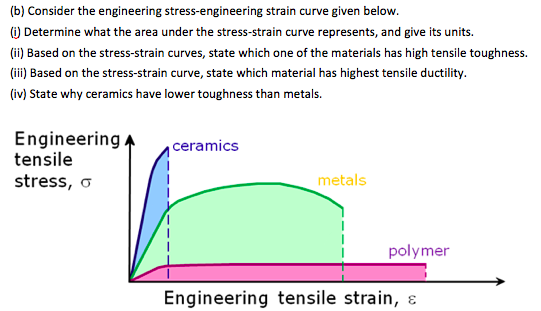
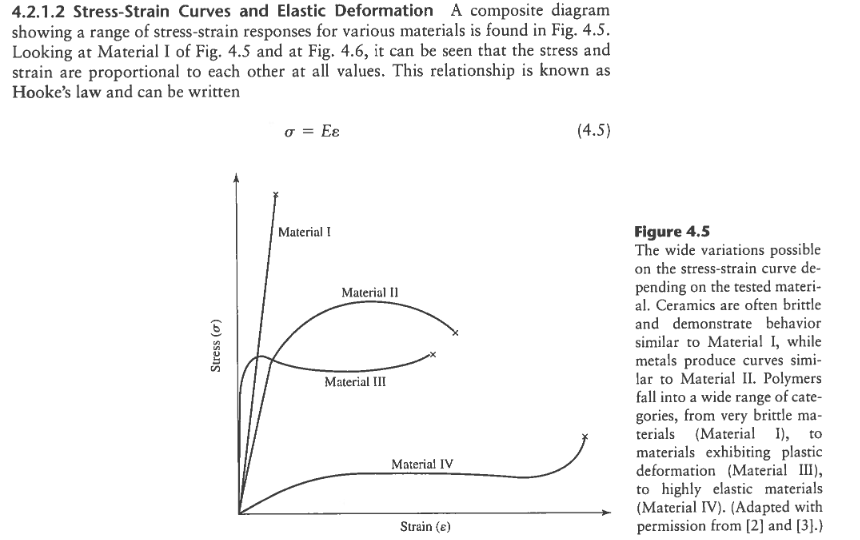
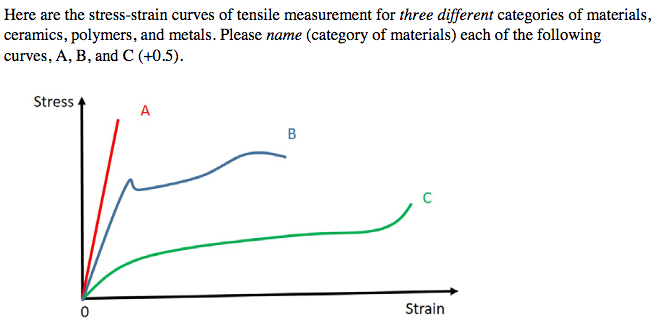
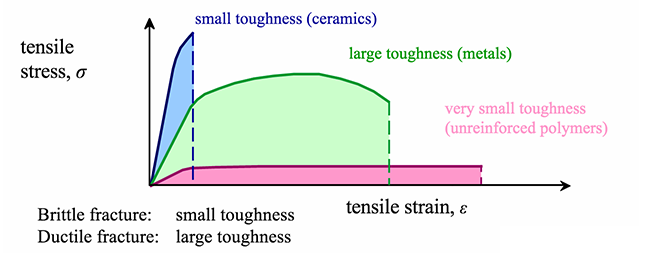
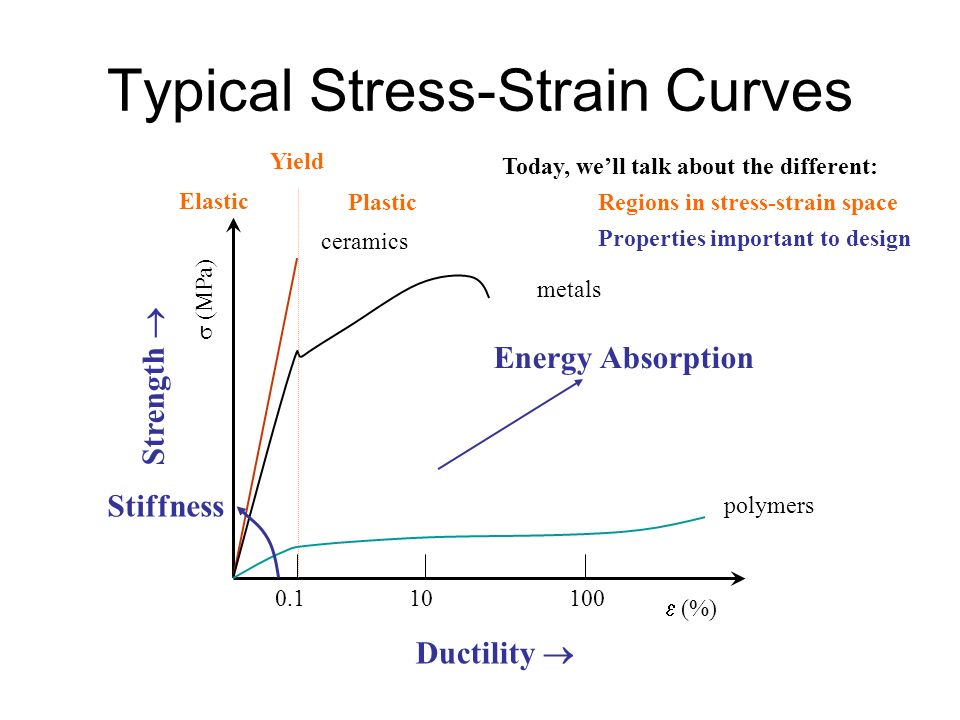
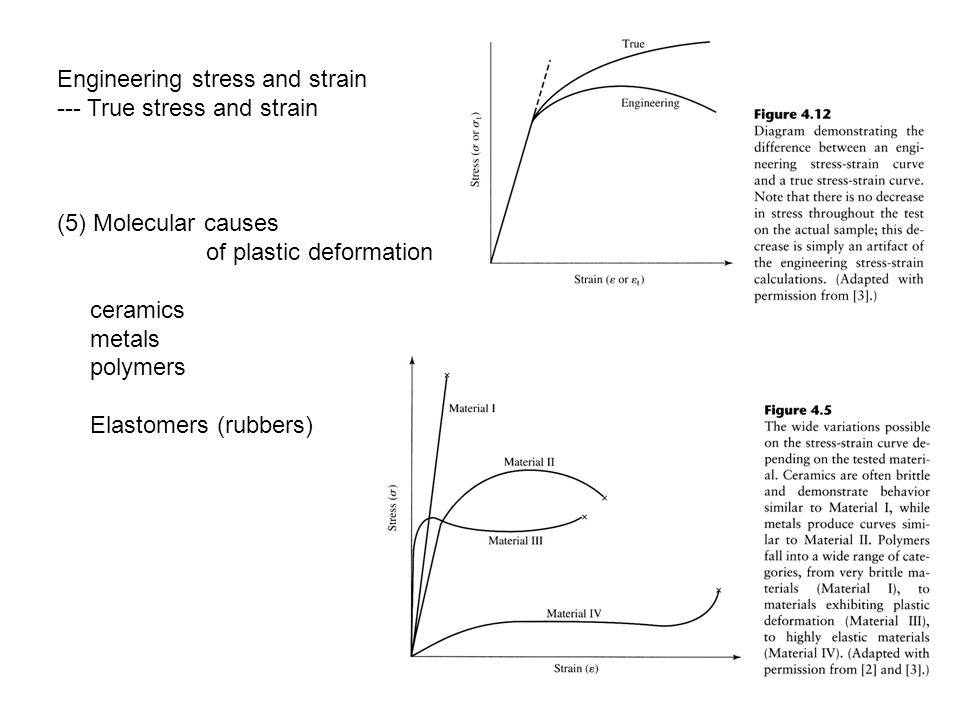
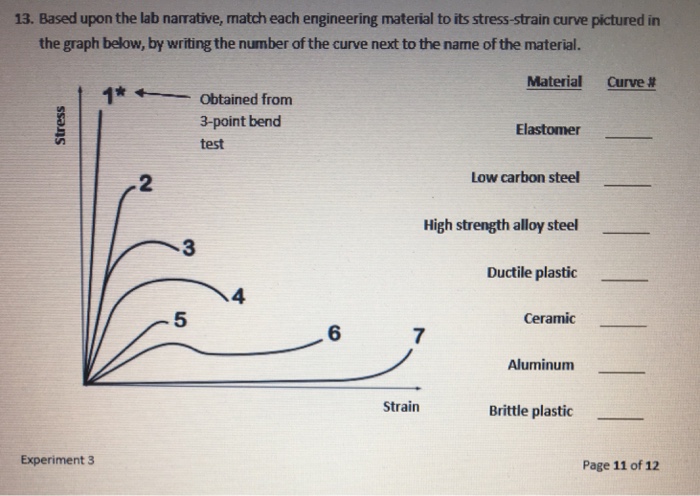
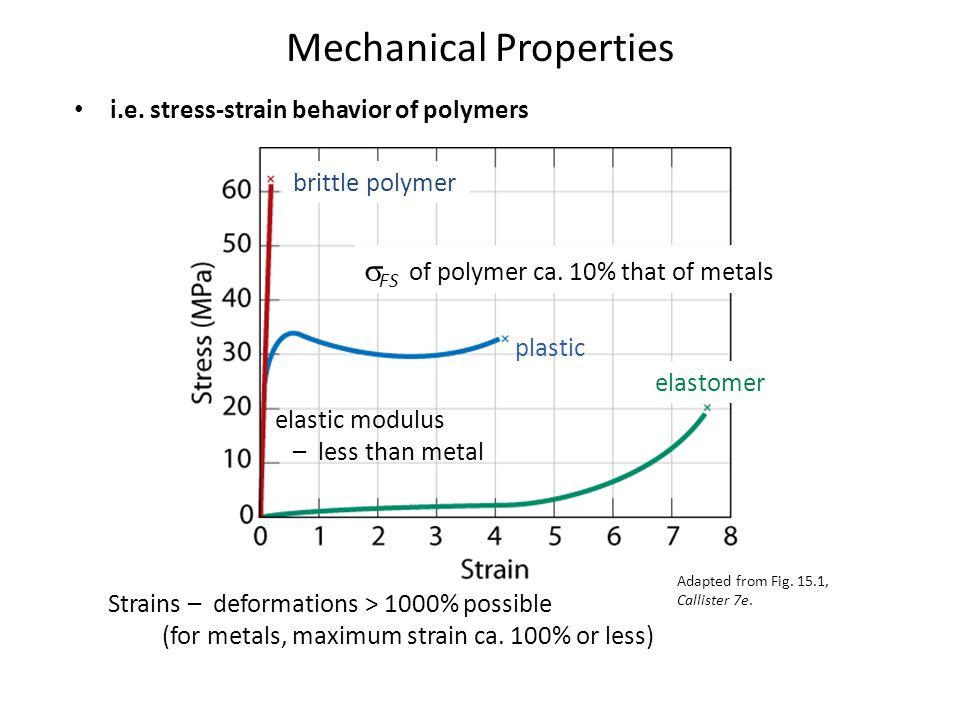
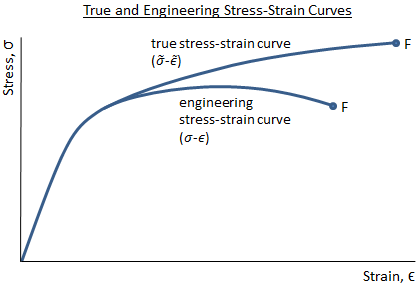
Specifically the stress strain curve shows the relationship of strain to stress for certain materials at specific properties such as temperature and pressure.
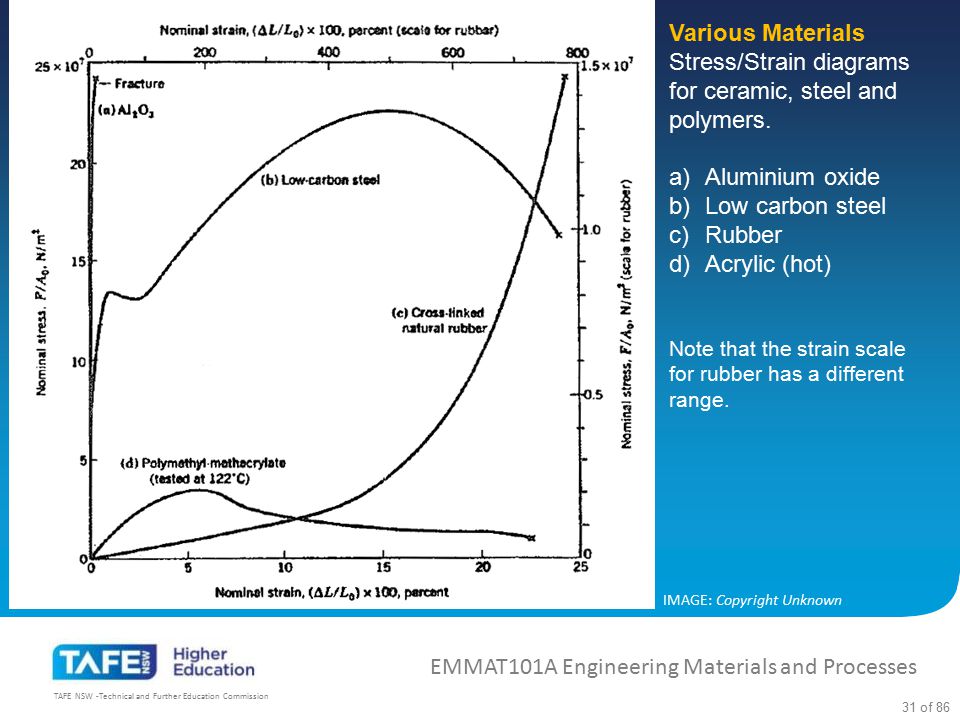
Engineering stress strain curve for ceramics.
2 stress strain curve for ceramics.
1 metals al alloy stress strain curve.
2 since both the stress and the strain are obtained by dividing the load and elongation by constant factors the load elongation curve will have the.
If we are talking about stressing the material and having it return to its original state we are talking about the material remaining in the elastic region of the stress strain curve.
In engineering and materials science a stress strain curve for a material gives the relationship between stress and strain it is obtained by gradually applying load to a test coupon and measuring the deformation from which the stress and strain can be determined see tensile testing these curves reveal many of the properties of a material such as the young s modulus the yield strength.
In engineering deformation refers to the change in size or shape of an object.
With one simple graph an engineer can understand many properties of a material under load applied force.
The elastic modulus the yield strength the ultimate tensile strength and the fracture strain are all clearly exhibited in an accurately constructed stress strain curve.
An example of the engineering stress strain curve for a typical engineering alloy is shown in figure 1.
It turns out that we can get the energy of elasticity by taking the area under the curve of the stress strain curve.
With a very short elastic region but highly capable of supporting huge stresses.
And finally analogous to ceramics are the stiff fibers and rigid plastics.
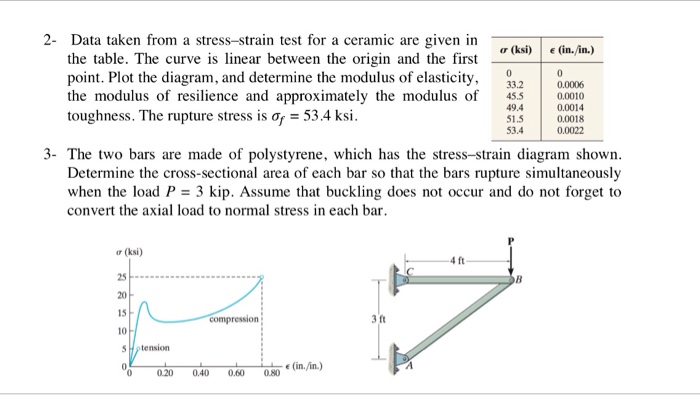
For brittle ceramics a three point bending apparatus shown in the figure below is used determine the stress strain behavior and the measurement results are used to calculate an equivalent modulus of elasticity.
From it some very important properties can be determined.
The strain used for the engineering stress strain curve is the average linear strain which is obtained by dividing the elongation of the gage length of the specimen d by its original length.